According to the Reading "the Us Economy:.." Which of the Following Is Not a Role of the Government:
About the Federal Reserve Organization
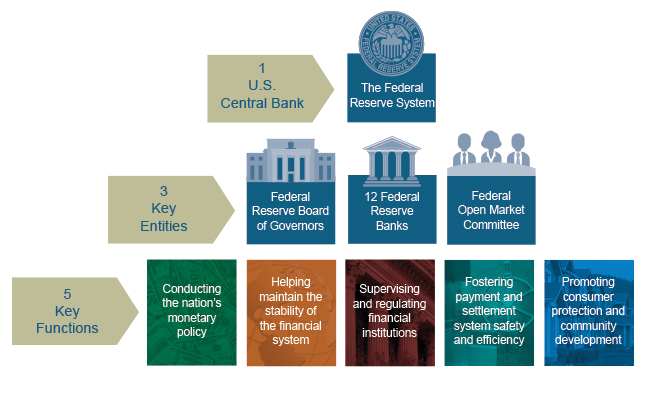
The Federal Reserve Organization is the central depository financial institution of the United States.
It performs five general functions to promote the effective operation of the U.Due south. economy and, more than generally, the public interest. The Federal Reserve
- conducts the nation'south monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates in the U.S. economy;
- promotes the stability of the financial arrangement and seeks to minimize and incorporate systemic risks through active monitoring and engagement in the U.Due south. and abroad;
- promotes the safety and soundness of individual fiscal institutions and monitors their impact on the financial system as a whole;
- fosters payment and settlement system safe and efficiency through services to the banking industry and the U.S. authorities that facilitate U.S.-dollar transactions and payments; and
- promotes consumer protection and community development through consumer-focused supervision and exam, inquiry and assay of emerging consumer bug and trends, community economic evolution activities, and the administration of consumer laws and regulations.
Read more in the 11th edition of Federal Reserve Organization The Fed Explained.
The Decentralized System Construction and Its Philosophy
In establishing the Federal Reserve Arrangement, the Us was divided geographically into 12 Districts, each with a separately incorporated Reserve Bank. District boundaries were based on prevailing trade regions that existed in 1913 and related economical considerations, and so they do not necessarily coincide with state lines.
As originally envisioned, each of the 12 Reserve Banks was intended to operate independently from the other Reserve Banks. Variation was expected in discount rates--the interest rate that commercial banks were charged for borrowing funds from a Reserve Bank. The setting of a separately determined discount charge per unit appropriate to each District was considered the most important tool of monetary policy at that fourth dimension. The concept of national economic policymaking was not well developed, and the impact of open market operations--purchases and sales of U.S. government securities--on policymaking was less significant.
As the nation's economy became more than integrated and more complex, through advances in applied science, communications, transportation, and financial services, the effective conduct of monetary policy began to require increased collaboration and coordination throughout the System. This was accomplished in part through revisions to the Federal Reserve Human activity in 1933 and 1935 that together created the modern-day Federal Open Market Commission (FOMC).
The Depository Institutions Deregulation and Budgetary Command Deed of 1980 (Monetary Control Human action) introduced an even greater degree of coordination among Reserve Banks with respect to the pricing of financial services offered to depository institutions. There has also been a tendency amidst Reserve Banks to centralize or consolidate many of their fiscal services and support functions and to standardize others. Reserve Banks have get more efficient by entering into intra-System service agreements that allocate responsibilities for services and functions that are national in scope amid each of the 12 Reserve Banks.
The U.S. Approach to Cardinal Cyberbanking
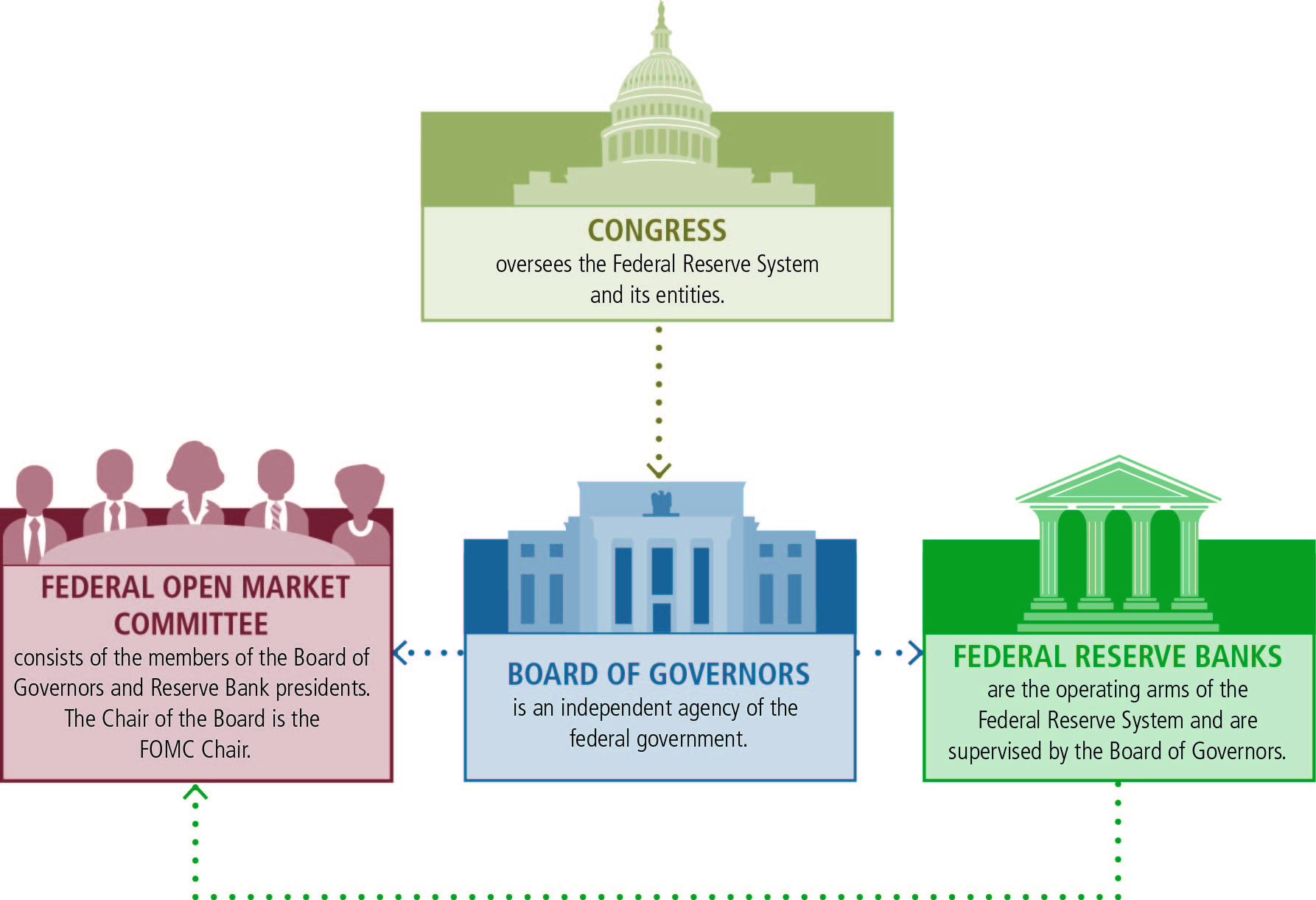
The framers of the Federal Reserve Act purposely rejected the concept of a unmarried central bank. Instead, they provided for a central banking "system" with three salient features: (ane) a primal governing Board, (two) a decentralized operating structure of 12 Reserve Banks, and (three) a combination of public and private characteristics.
Although parts of the Federal Reserve Arrangement share some characteristics with private-sector entities, the Federal Reserve was established to serve the public interest.
There are three key entities in the Federal Reserve System: the Board of Governors, the Federal Reserve Banks (Reserve Banks), and the Federal Open Market place Committee (FOMC). The Lath of Governors, an agency of the federal government that reports to and is directly answerable to Congress, provides general guidance for the System and oversees the 12 Reserve Banks.
Within the System, certain responsibilities are shared between the Board of Governors in Washington, D.C., whose members are appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate, and the Federal Reserve Banks and Branches, which constitute the System'south operating presence effectually the country. While the Federal Reserve has frequent communication with executive branch and congressional officials, its decisions are fabricated independently.
The Three Key Federal Reserve Entities
The Federal Reserve Board of Governors (Board of Governors), the Federal Reserve Banks (Reserve Banks), and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) make decisions that help promote the wellness of the U.South. economy and the stability of the U.S. financial system.
Other Significant Entities Contributing to Federal Reserve Functions
Ii other groups play important roles in the Federal Reserve Organisation's cadre functions:
- depository institutions--banks, thrifts, and credit unions; and
- Federal Reserve System advisory committees, which make recommendations to the Lath of Governors and to the Reserve Banks regarding the System'south responsibilities.
Depository Institutions
Depository institutions offer transaction, or checking, accounts to the public, and may maintain accounts of their own at their local Federal Reserve Banks. Depository institutions are required to meet reserve requirements--that is, to keep a certain amount of greenbacks on hand or in an business relationship at a Reserve Bank based on the total balances in the checking accounts they agree.
Depository institutions that take higher balances in their Reserve Banking company business relationship than they demand to meet reserve requirements may lend to other depository institutions that need those funds to satisfy their own reserve requirements. This rate influences interest rates, nugget prices and wealth, exchange rates, and thereby, aggregate demand in the economy. The FOMC sets a target for the federal funds rate at its meetings and authorizes actions called open market operations to reach that target.
Informational Councils
Four advisory councils help and suggest the Board on matters of public policy.
- Federal Advisory Council (FAC). This quango, established by the Federal Reserve Deed, comprises 12 representatives of the banking manufacture. The FAC usually meets with the Board four times a year, as required by constabulary. Annually, each Reserve Bank chooses one person to stand for its District on the FAC. FAC members customarily serve 3 i-year terms and elect their own officers.
- Customs Depository Institutions Informational Council (CDIAC). The CDIAC was originally established past the Board of Governors to obtain information and views from thrift institutions (savings and loan institutions and mutual savings banks) and credit unions. More recently, its membership has expanded to include customs banks. Similar the FAC, the CDIAC provides the Board of Governors with firsthand insight and information about the economic system, lending atmospheric condition, and other bug.
- Model Validation Council. This council was established by the Board of Governors in 2012 to provide proficient and independent communication on its process to rigorously assess the models used in stress tests of cyberbanking institutions. Stress tests are required under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. The quango is intended to ameliorate the quality of stress tests and thereby strengthen confidence in the stress-testing program.
- Customs Advisory Council (CAC). This quango was formed past the Federal Reserve Board in 2022 to offer diverse perspectives on the economic circumstances and financial services needs of consumers and communities, with a particular focus on the concerns of low- and moderate-income populations. The CAC complements the FAC and CDIAC, whose members represent depository institutions. The CAC meets semiannually with members of the Board of Governors. The fifteen CAC members serve staggered three-twelvemonth terms and are selected by the Board through a public nomination process.
Federal Reserve Banks also have their own advisory committees. Perchance the most of import of these are committees that advise the Banks on agronomical, small business, and labor matters. The Federal Reserve Board solicits the views of each of these committees biannually.
Back to Top
Terminal Update: September ten, 2021
Source: https://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/structure-federal-reserve-system.htm
0 Response to "According to the Reading "the Us Economy:.." Which of the Following Is Not a Role of the Government:"
Post a Comment